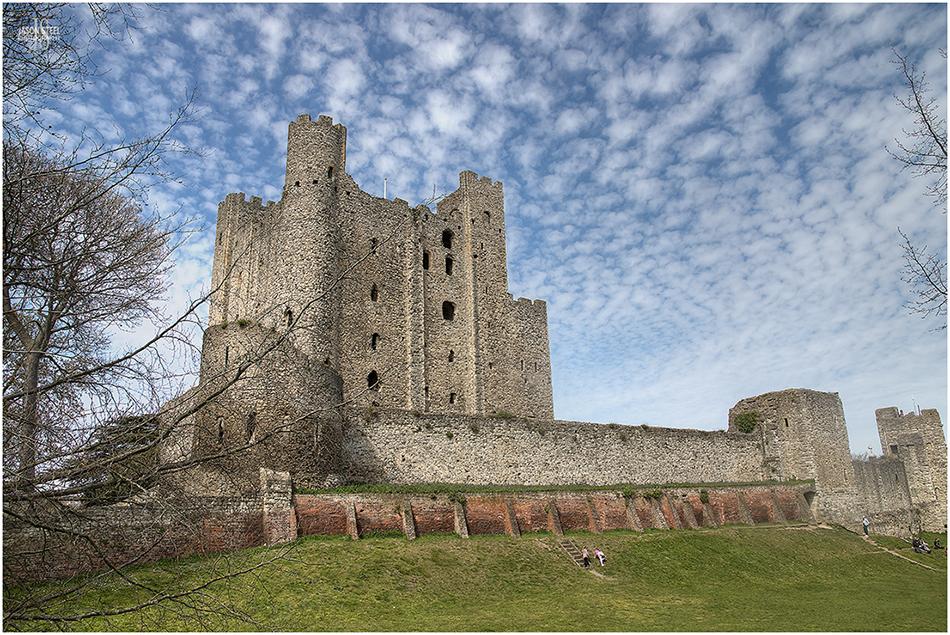

Rochester Castle's keep was built around 1127 AD by William of Corbeil, Archbishop of Canterbury. Photo taken April 2021
Rochester Castle
Rochester Castle is located on the River Medway and Watling Street in Kent. The site has been home to a castle since 1088, shortly after the Norman invasion. It's Norman keep was built as an armed fortress from Kentish ragstone around 1127 AD by William of Corbeil, Archbishop of Canterbury, under the watch of Henry I. It stands 113ft high. In 2012 the castle was held at siege by King John's garrison of rebel barons. During this size the southern corner was brought crashing down by a fire built beneath the wall. The defenders held on for a further two months before being starved into surrendering. The castle was rebuilt by Henry III and Edward I and remained an active fortress until the sixteenth century.
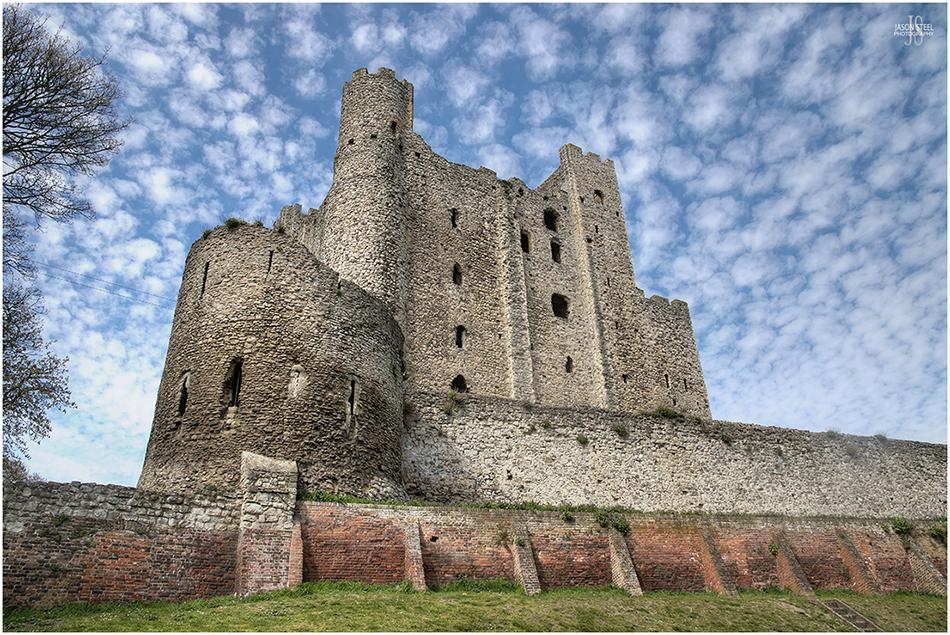

Rochester Castle's keep
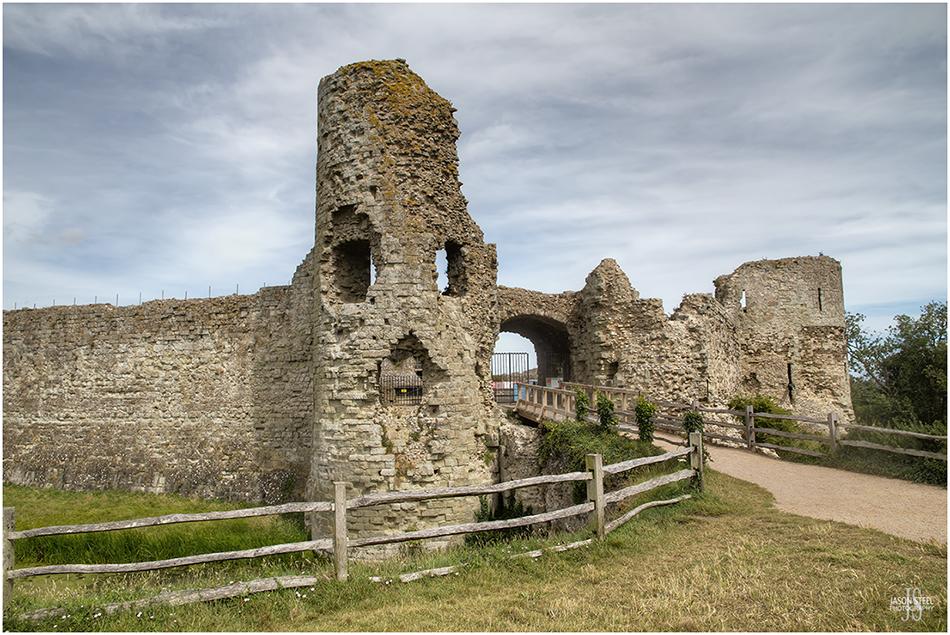

The gatehouse to the inner bailey at Pevensey Castle was probably built around 1200 AD. Photo taken 26th July 2020
Pevensey Castle
The site of Pevensey Castle is located near Hastings, Sussex, and was originally a Roman Fort dating back as far as AD 290. After the Normans invaded in 1066 the fort was strengthened but the medieval stone castle we see today wasn't constructed until at least 1129 - 1199. It's uncertain which stone walls that still stand today were those originally built in the early years of the castle's history.
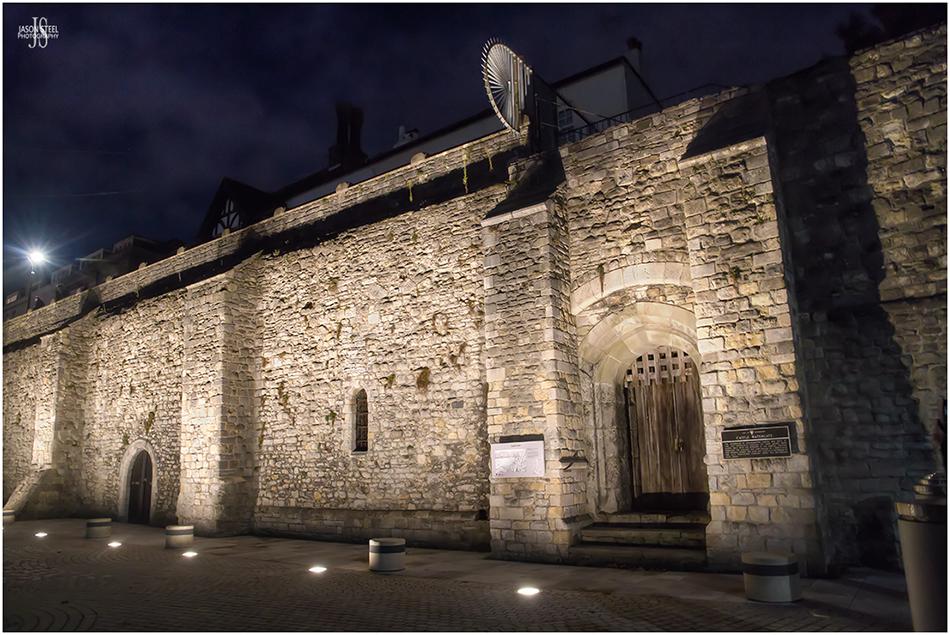

Southampton Castle Watergate, October 2020
Southampton Castle
Originally a wooden Motte & Bailey design by the end of 12th Century the castle was replaced by a stone keep as part of England's coastal defences. By the 1600s the castle had fallen into a bad state of disrepair and was sold off to property developers. Only fragments of Southampton Castle now remain, including the Watergate, which is surrounded by modern buildings including the WestQuay shopping Centre and Cinema complex.
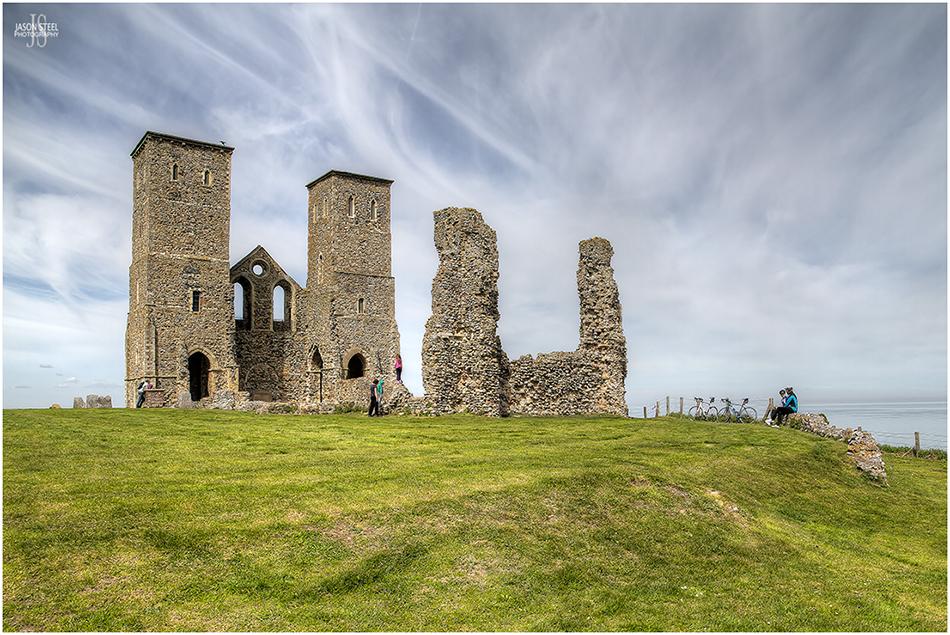

Reculver Towers, Reculver Bay, Kent. May 2016.
Reculver Towers
In the early part of the 3rd Century the site was home to a Roman Fort built with flint walls and surrounded by two ditches. By the 5th Century the Romans had abandoned its defences of the English coast and the fort was left unused. It 669 the fort became the basis for an Anglo-Saxon monastery. Remodelling of the church in the 12th Century saw the addition of the twin towers. The medieval church was partly demolished in 1805 when most of the stone was reclaimed for use building a new church on higher ground at Hillborough. The twin towers are now all that remains of the former fort and monastery after much of the site has been lost to the sea as a result of coastal erosion.
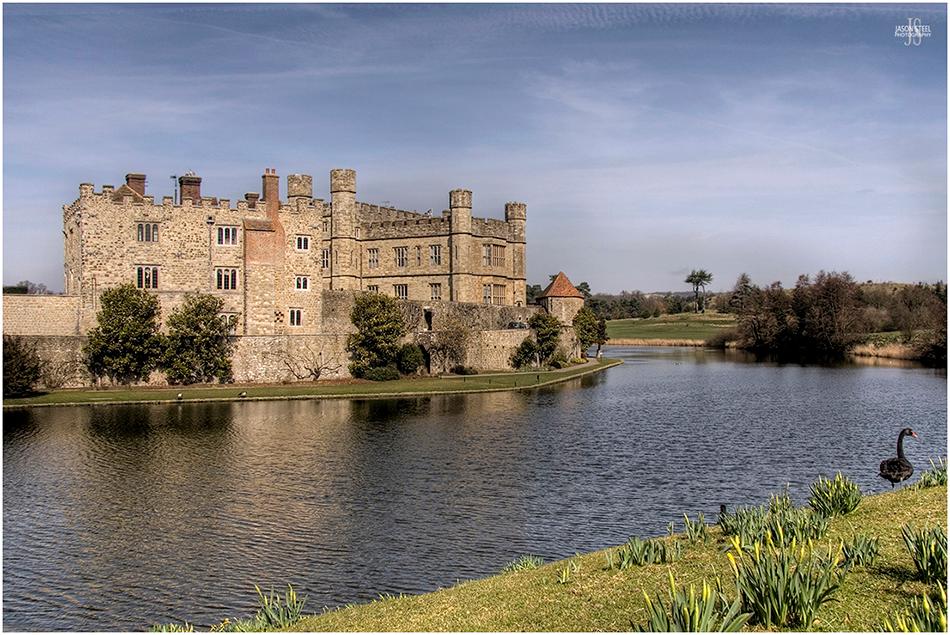

Leeds Castle, Maidstone, Kent. March 2009.
Leeds Castle
Originally completed in 1139 Leeds Castle has since undergone many changes, upgrades and remodelling. These major changes included turning the castle into a Jacobean House in the 17th Century, and then converted into a Georgian mansion in the 18th Century. The original medieval buildings were finally demolished and the New Castle was built within the walls and mote surrounding the grounds in 1820. The castle has been a residence of many owners in its lifetime including Henry VIII who transformed the castle from a fortified stronghold into a magnificent royal palace. In 1970 Leeds Castle was opened up to the public and became a tourist attraction.
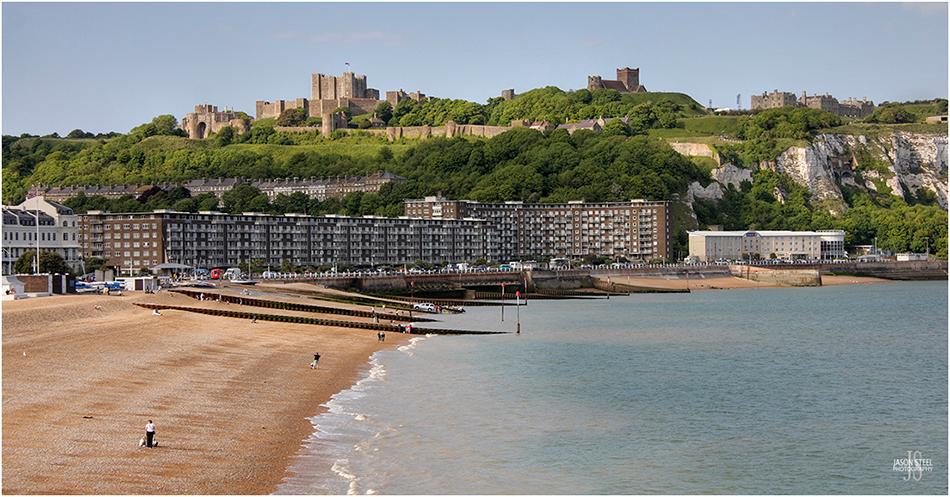

Dover Castle, Kent. May 2009.
Dover Castle
Standing at the top of Kent's iconic White Cliffs Dover Castle is a Medieval Castle originally built in 11th Century which had been a site of fortifications since the Iron Age. The castle you see now was built largely by Henry II and was completed in 1188 and stood as both a residential site and military stronghold. It remained a military site until after WWII. There is some dispute as to whether Dover Castle or Winsor Castle is the largest remaining castle in England.
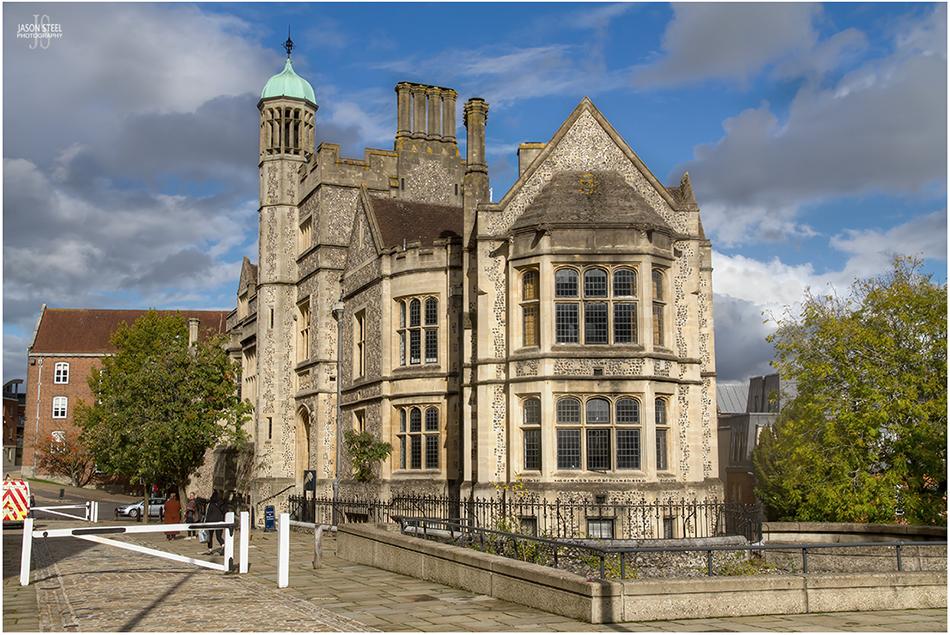

Castle Hill Offices, County Hall, on the site of the former Winchester Castle, Kent. October 2020.
Winchester Castle
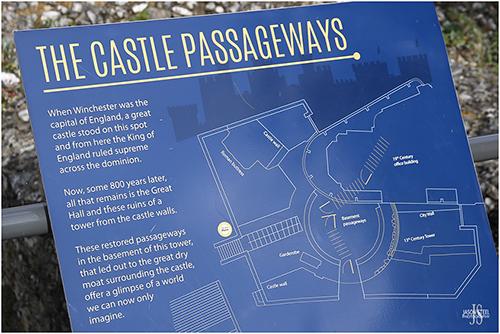
The Castle Hill Offices at County Hall were completed in 1895, and stand on what was once the site of Winchester Castle. Winchester Castle was originally founded in 1067 by William the Conqueror. In 1222 Henry III extended the castle and began construction of the Great Hall, one of Britain's earliest Gothic-styled halls.
In 1646 Oliver Cromwell ordered the destruction of Winchester Castle immediately after the end of the English Civil War. Today only the Great Hall remains along with the ruins of a tower which formed part of the old castle wall, which can now be seen adjacent to, and below the County Hall. Part of these tower ruins include the restored passageways that once led out to the great dry moat that surrounded the castle walls.
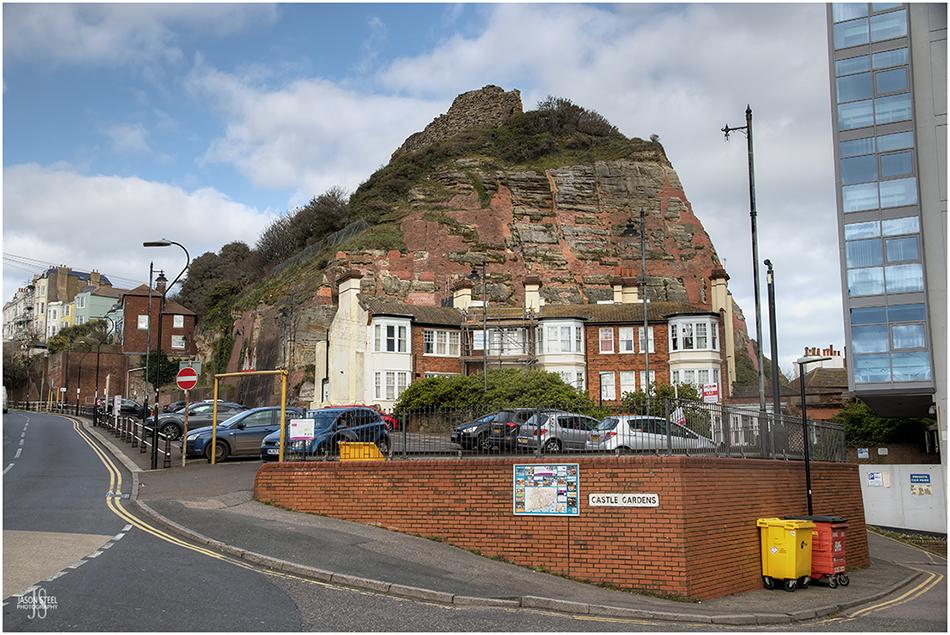

Hastings Castle, East Sussex. 4th April 2021.
Hastings Castle
Hastings Castle was originally a wooden fortress built by William the Conqueror in 1066 when he landed in Pevensey. After the Battle of Hastings, and the coronation of William, he immediately ordered that the quickly erected wooded structure be replaced with a stone castle which included a stone church within the grounds.
In 1216 King John ordered the castle to be dismantled fearing it would fall into the hands of the French should they invade Britain. The castle was rebuilt in 1225 by Henry III and then later partially dismantled again by Edward II. Savage storms of the 13th Century saw Hastings Harbour destroyed and much of what remained of the castle fell into the sea. Henry VIII ordered the church building be destroyed when he declared himself the head of the Church of England. The castle suffered further damage in bombing raids during WWII and Hastings Castle was finally bought and preserved by the Hastings Corporation in 1951 and became a tourist attraction.
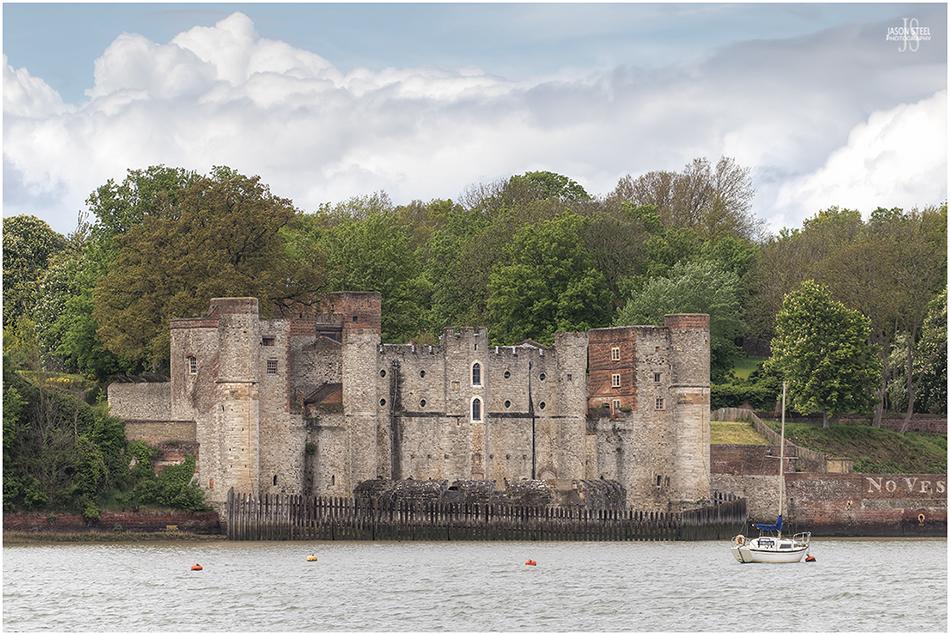

Upnor Castle, Upnor, Rochester, Kent. 16th May 2021.
Upnor Castle
Upnor Castle is a rare example of an Elizabethan Artillery Fort and was constructed in 1559 and then redeveloped from 1599-1601. It was originally built on the edge of the River Medway to protect both the dockyard and Royal Navy warships moored at Chatham Docks. Unfortunately the 80 men and 20 canons at Upnor Castle were unable to prevent the Dutch fleet from sailing past it in 1667 when they launched an attack on the British fleet at anchor. The Dutch were able to capture two of the Royal Navy's ships and burn the rest before being forced to flee from heavy gunfire from the castle. This defeat by the British lead to the construction of stronger fortifications further up the river and Upnor Castle was eventually resigned to the purpose of an ammunition store. It remained in military service until 1945 until it became the property of English Heritage and was opened to the public. Events at the castle are now managed by Medway Council.
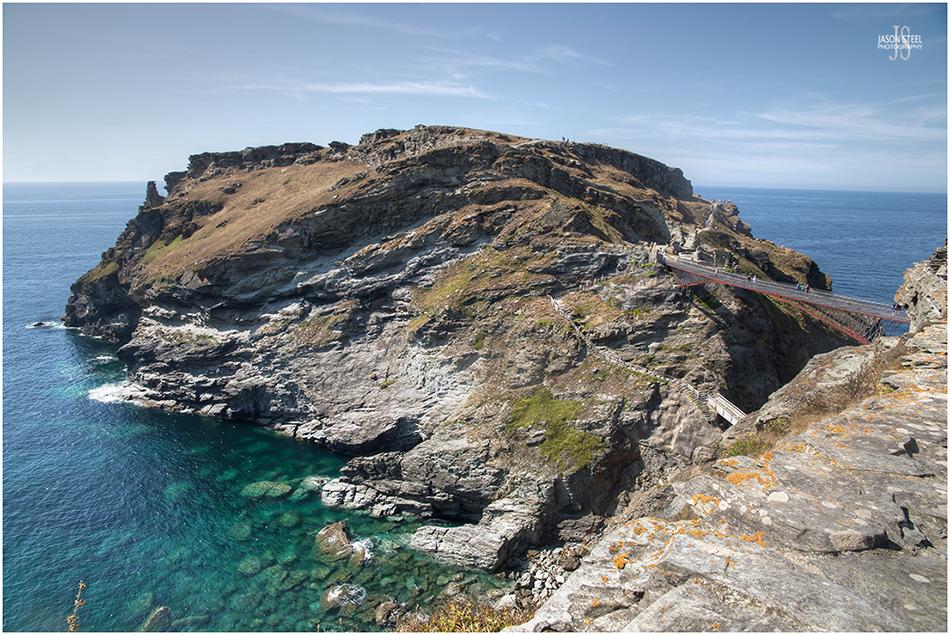

Tintagel Castle, Tintagel Island, North Cornwall. 9th August 2022.
Tintagel Castle
Tintagel Castle
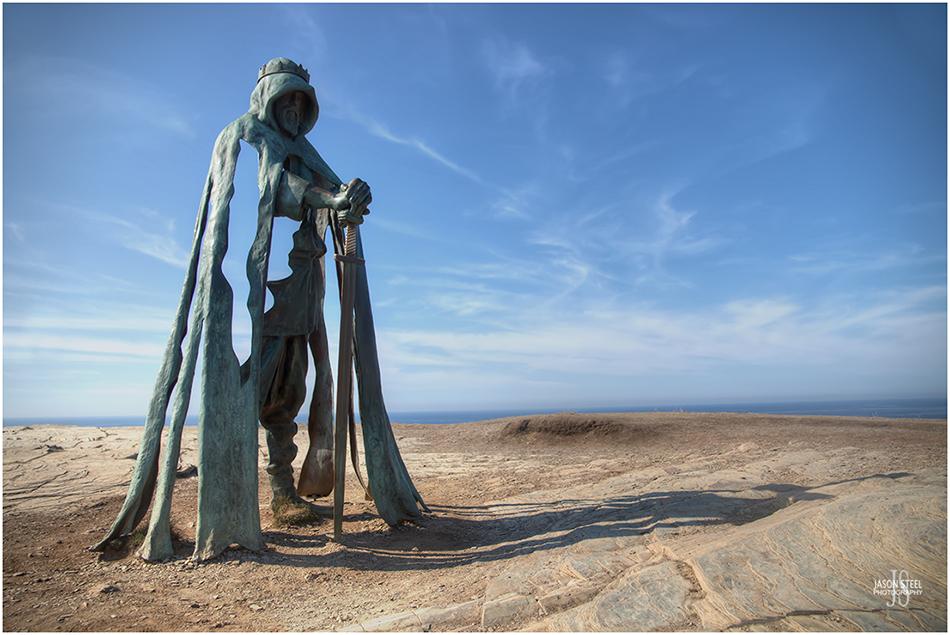

King Arthur's statue at Tintagel Castle, Tintagel Island, North Cornwall. 9th August 2022.
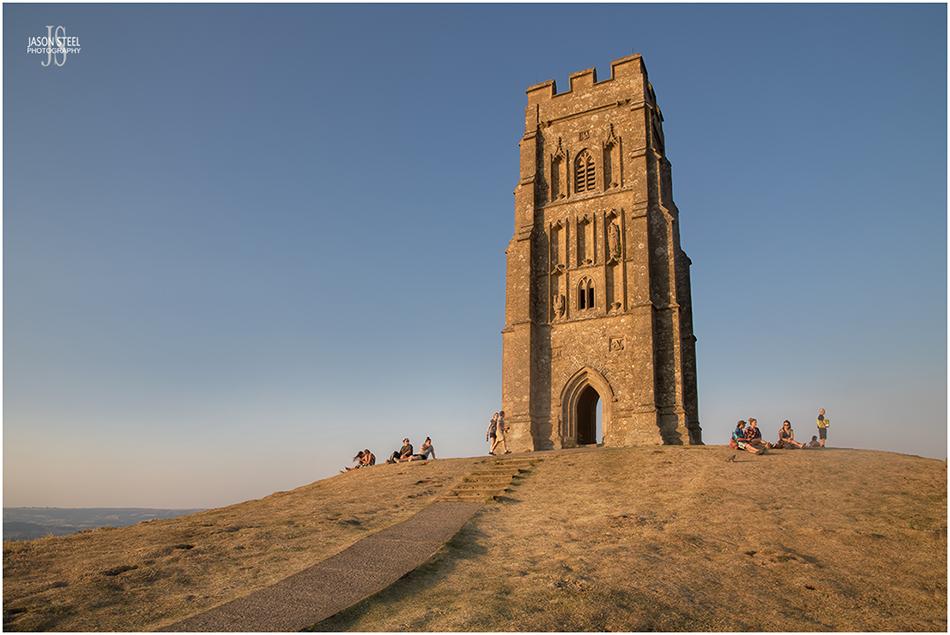

St Michael's Tower. Glastonbury Tor, Glastonbury, 12th August 2022
St Michael's Tower
St Michael's Tower.
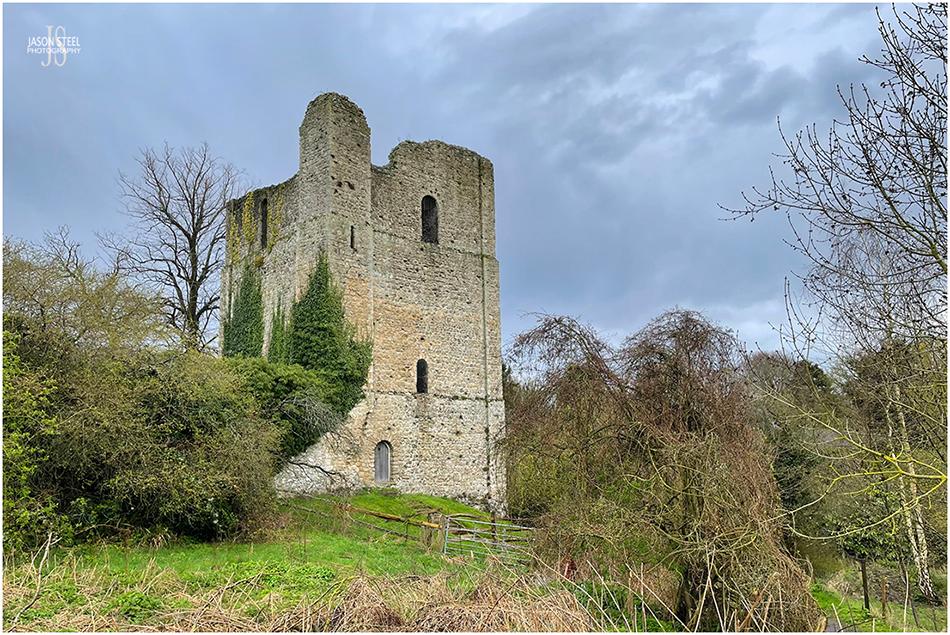

St. Leonard' s Tower, West Malling, Kent. 6th April 2023 - (iPhone photo)
St. Leonard' s Tower
St. Leonard' s Tower sits in the countryside village of West Malling in Kent. The Tower was built between the years 1077 - 1108. There are two theories as to what the tower used to be. Most people believe the tower is what remains of a castle, built by Gundulf, who at the time was the Bishop of Rochester. Gundulf also founded the nearby abbey. The other theory is that the tower may have been built by Bishop Odo of Bayeux, the half-brother of William the Conqueror. The tower has limited defences and limited suitability as a residential dwelling, so it's likely that the tower was used as an administrative centre. St. Leonard' s Tower is under the care of the English Heritage, and the site is free to access.
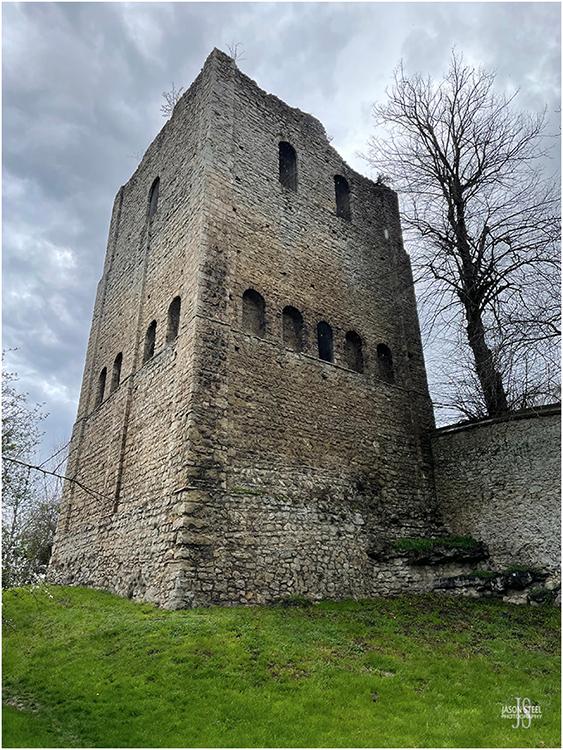

St. Leonard' s Tower, West Malling, Kent. 6th April 2023 - (iPhone photo)
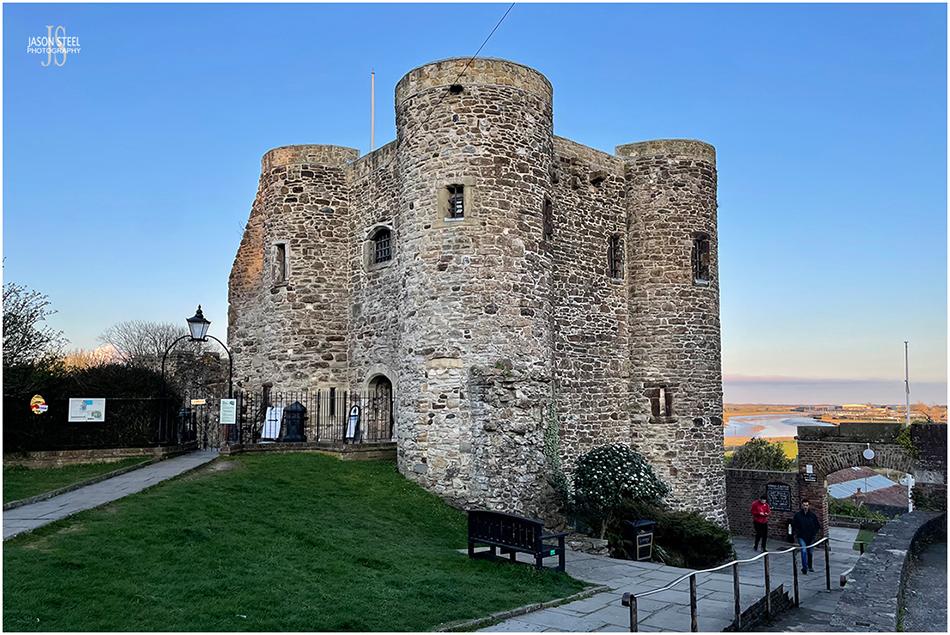

Ypres Tower, Rye Castle, East Sussex. 8th April 2023 - (iPhone photo)
Ypres Tower, Rye Castle
The town of Rye was officially recognised by King Edward I in 1289, and was given tax privileges in exchange for services to the royal ships. The building of Rye Castle was started in the mid 13th century, under the direction of King Henry III (1216-1272), as part of the town fortifications against invaders. The castle was known then as Baddings Tower. In 1377 the town of Rye was successfully invaded by the French and much of the town was destroyed. The castle was one of the few buildings to survive the invasion. In 1430 Rye Castle was sold to the Frenchman, Jean d'Ypres, and the tower became known as Ypres Tower. In more recent years the Ypres Tower at Rye Castle has been used as a fortified home, a courthouse, a prison, and a museum. The site is free to enter, but there is a charge to enter the Ypres Tower itself.
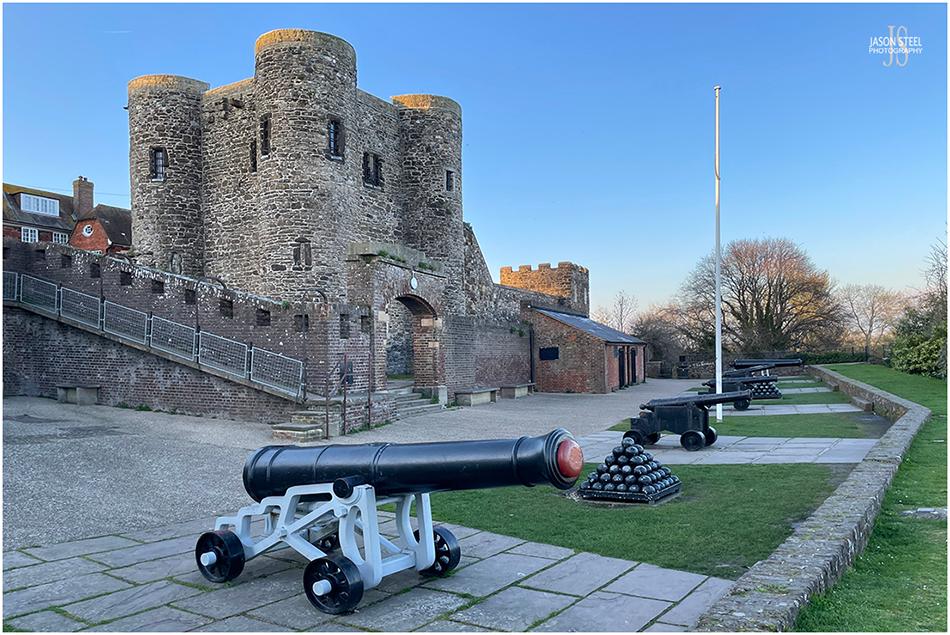

Ypres Tower, Rye Castle, East Sussex. 8th April 2023 - (iPhone photo)
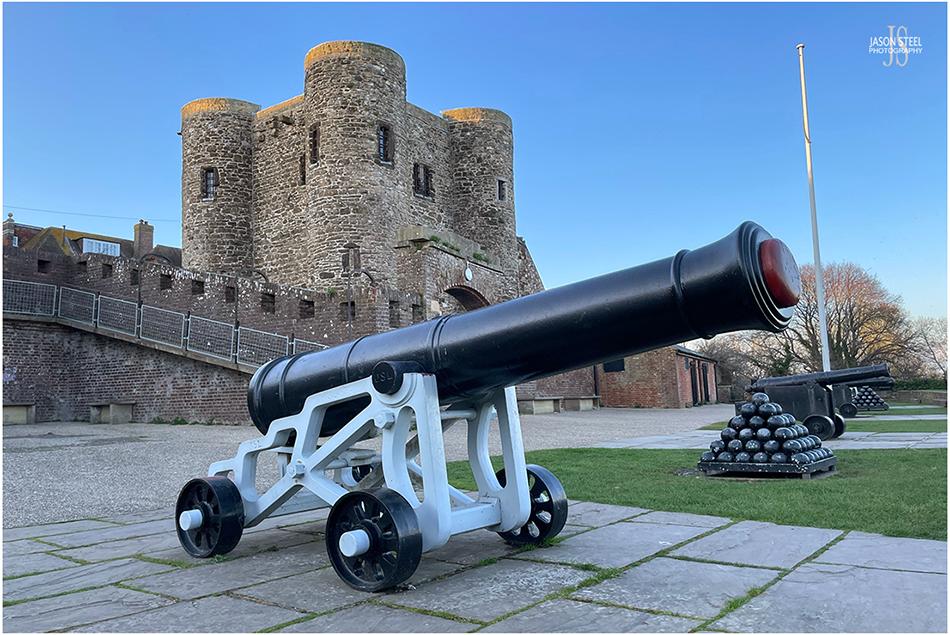

Ypres Tower, Rye Castle, East Sussex. 8th April 2023 - (iPhone photo)
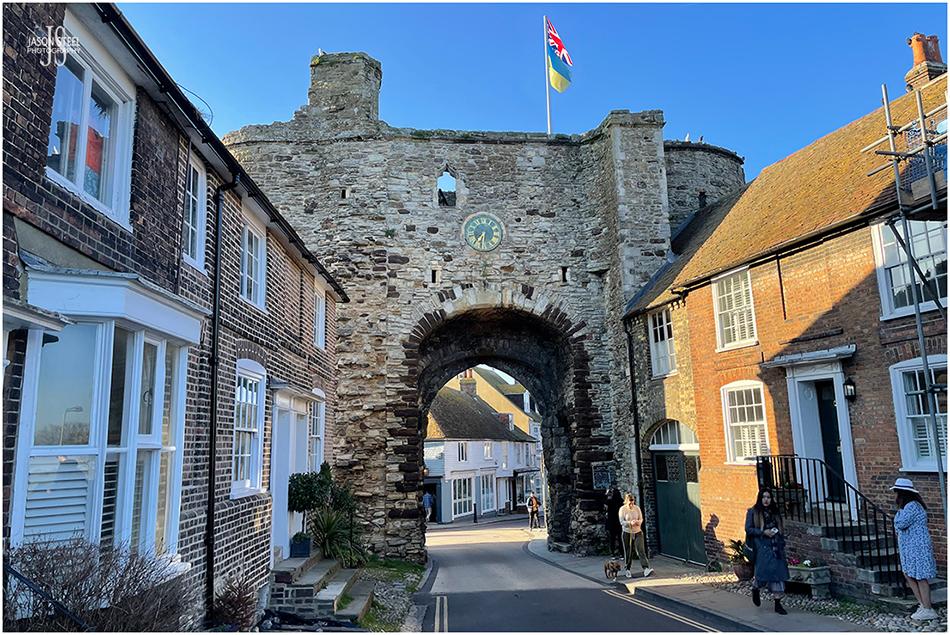

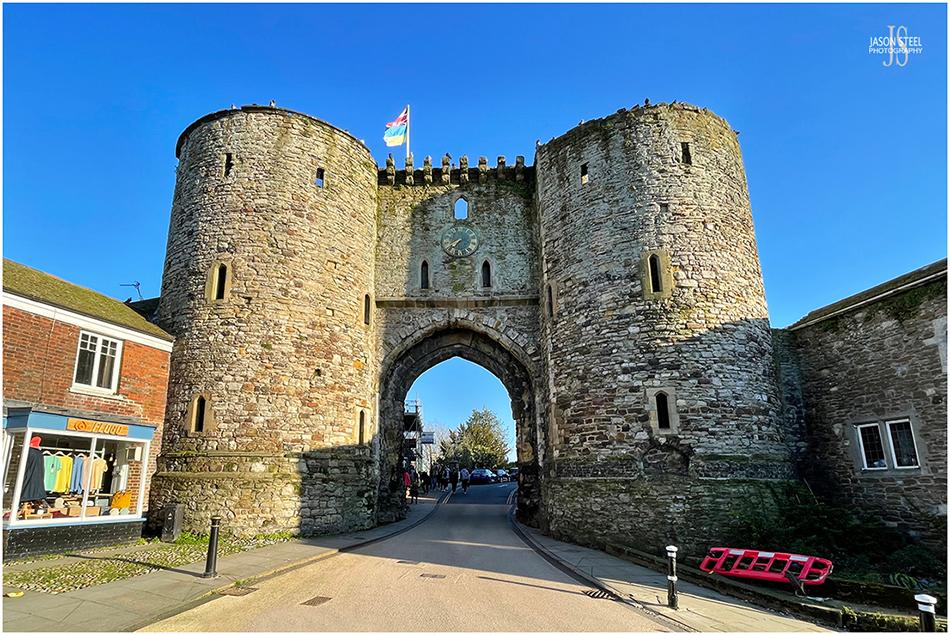
Landgate, Rye, East Sussex. 8th April 2023 - (iPhone photo)
The Landgate entrance to Rye town is the only surviving of four, original fortified entrances to Rye town. The Landgate dates from 1329, and was constructed under the direction King Edward III (1327-1377), to further fortify the town. Originally this Landgate included gates, a portcullis and a drawbridge, as part of its defences. As seen in this photo the flags of both Great Britain and Ukraine were flown above the tower during 2022 and 2023, in support of Ukraine, that was at the time at War with Russia, since being invaded by the Russian army on February 24th 2022.

Landgate, Rye, East Sussex. 8th April 2023 - (iPhone photo)
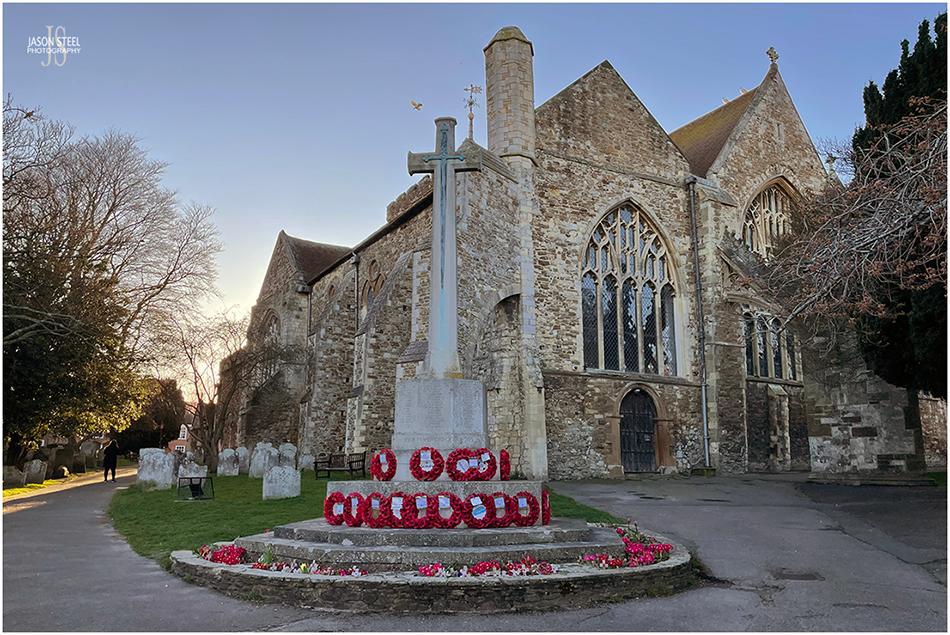

Church of Saint Mary, Rye, East Sussex. 8th April 2023 - (iPhone photo)
Church of Saint Mary
The Church of Saint Mary
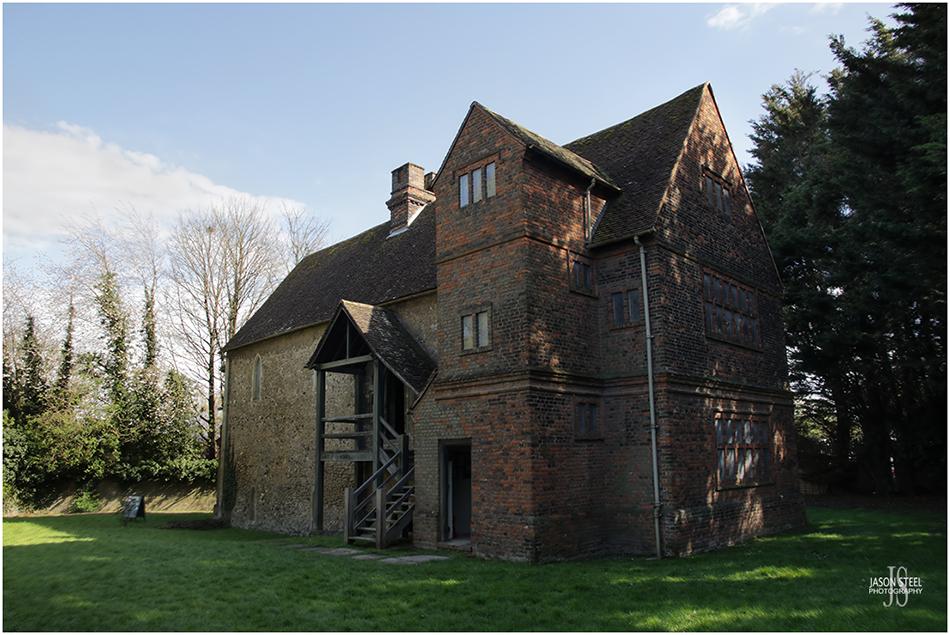


Temple Manor, Strood, Kent. 13th April 2023
Temple Manor
The site of Temple Manor is located just west of the River Medway, and was originally given to the Templars Order by Henry II around 1158. The original block of Temple Manor was built around 1240. It was built to provide food, shelter, and fresh horses for members of the order, travelling along Watling Street, from London and Dover, as part of the work of the crusades. In 1308 Edward II seized Templar land and properties and Temple Manor was given to the Earl of Pembroke. By 1312 Pope Clement V dissolved the Order of the Temple. Temple Manor passed through many ownerships, and served many purposes over the next 300 years.
In 1642 was bought by the Blake family, who added the brick extensions and the large fireplace and chimney. After WWII Temple Manor was in a terrible state of disrepair and the roof had completely collapsed. In 1950 Temple Manor was listed as grade 1 and was given to the Ministry of Works. Between 1950 and 1960 the building was completely restored and opened to the public. Medway Council have taken over management of the property since 1998 and today the building is owned by the English Heritage and is open to the public at weekends during the summer months, and is free to enter.
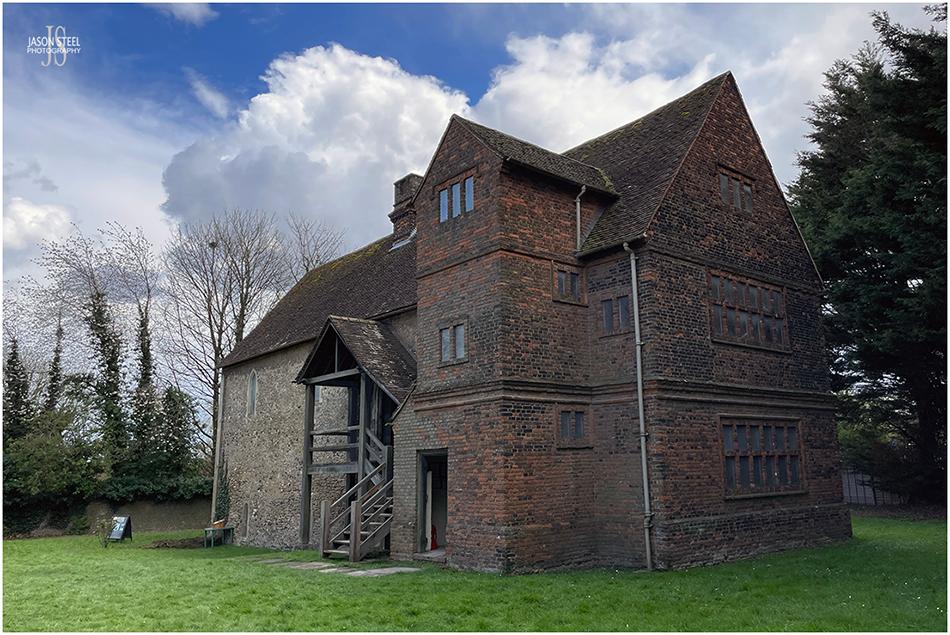

iPhone photo - Temple Manor, Strood, Kent. 13th April 2023
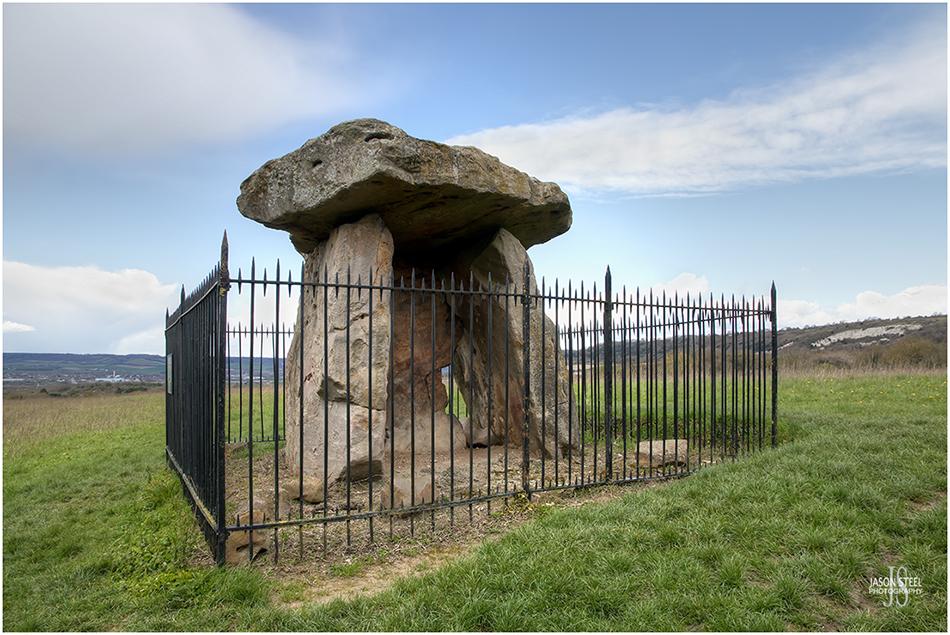

Kit's Coty House, Aylesford, Kent. 13th April 2023
Kit's Coty House
Kit's Coty House, and the closely located Little Kit's Coty House, are the remains of two megalithic communal burial chambers. They date back to around 6000 years ago, at the start of the Neolithic period. Both structures are located in the middle of fields overlooking the Medway Valley. These communal burial chambers are known as Long barrows, and they were built between 4000 and 3000 BC. They are among the oldest of prehistoric monuments in Britain and were the burial places of Britain's earliest farming communities, a tradition brought over from Europe. These structures are two out of six, in a collection of local large stones structures (or Megalithics), known as the Medway Megaliths. The stones were fenced off in 1885 to prevent further vandalism and protect the stones for future generations to enjoy and appreciate. The site of Kit's Coty House is owned by the English Heritage, and is free to access.
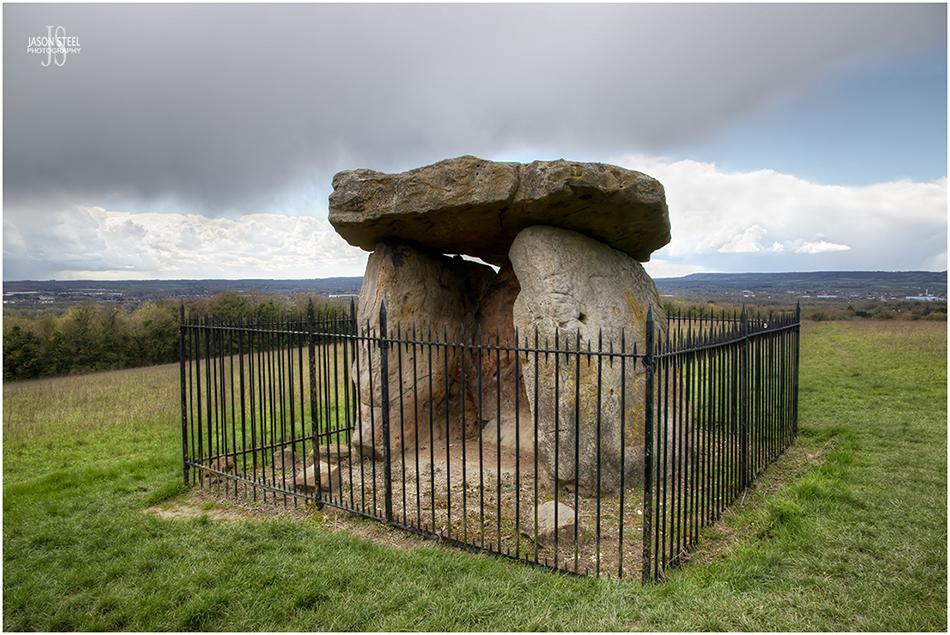

Kit's Coty House, Aylesford, Kent. 13th April 2023